AML and KYC: Ensuring Compliance and Combating Financial Crimes
In an increasingly complex and interconnected world, financial institutions and businesses face significant challenges in ensuring compliance, preventing financial crimes, and maintaining the integrity of the global financial system. Two essential components in this battle are Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti Money Laundering (AML) practices.
KYC refers to the process of verifying the identity of customers and assessing the risks associated with their activities. It enables financial institutions to gather crucial information about their customers, ensuring transparency and accountability. On the other hand, AML focuses on detecting, preventing, and reporting money laundering activities, which involve disguising the origins of illicit funds.
This article delves into AML and KYC, highlighting their importance in combatting financial crimes. We will explore both practices' objectives, regulations, and requirements. Additionally, we will examine the differences between AML and KYC, where and when they are required, and the role of technology in facilitating compliance.
By unravelling the complexities of AML and KYC, this article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of their significance, the need for compliance, and the tools available to mitigate risks and ensure regulatory adherence. Let us embark on a journey to uncover the power of AML and KYC in safeguarding the financial system and preventing illicit activities.
What is Know Your Customer (KYC)?
KYC in a Nutshell
The Know Your Customer (KYC) process is an essential undertaking by financial institutions and businesses to authenticate the identities of their customers and evaluate the potential risks associated with unlawful activities. This procedure encompasses the gathering and validation of diverse customer information, including identification documents, proof of address, and comprehensive financial details.
In order to ensure regulatory compliance and mitigate risks, financial institutions and businesses embark on the crucial process known as Know Your Customer (KYC). Through KYC, these entities diligently verify the identities of their customers while carefully assessing the potential threats posed by illicit activities. The cornerstone of this process lies in the meticulous collection and validation of customer information, encompassing crucial elements such as identification documents, proofs of address, and comprehensive financial details. By adhering to robust KYC practices, organizations can establish a secure and trustworthy environment, safeguarding themselves and their stakeholders from the risks associated with financial crimes.
The Objectives of KYC
The primary objectives of Know Your Customer (KYC) encompass three essential aspects:
- Customer Identification: One of the fundamental goals of KYC is to enable financial institutions and businesses to accurately identify their customers and validate their identities. By implementing robust customer identification processes, organizations can ensure that they comprehensively understand who their customers are.
- Risk Assessment: Another crucial objective of KYC is to evaluate the risk profile associated with each customer. This entails conducting a thorough assessment to identify potential risks related to money laundering, terrorist financing, or other illicit activities. By comprehensively evaluating the risk factors, organizations can implement appropriate risk mitigation measures.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to financial authorities' legal and regulatory requirements is a cornerstone of KYC. Financial institutions and businesses must ensure compliance with the applicable regulations and guidelines to prevent financial crimes and maintain the financial system's integrity. By implementing robust KYC processes, organizations demonstrate their commitment to regulatory compliance and contribute to the overall stability of the financial ecosystem.
Through the fulfilment of these primary objectives, KYC serves as a critical mechanism for financial institutions and businesses to protect themselves, their customers, and the broader financial system from the risks associated with illicit activities. By adopting a proactive approach to customer identification, risk assessment, and regulatory compliance, organizations can enhance their security measures and foster trust within the financial landscape.
What is Anti Money Laundering (AML)?
AML in a Nutshell
Anti Money Laundering (AML) encompasses a comprehensive framework of regulations, policies, and procedures that are put in place to effectively identify, deter, and report instances of money laundering. This illicit activity involves concealing the unlawful origins of funds, aiming to present them as legitimate within the financial system. Through the implementation of robust AML measures, including enhanced due diligence, transaction monitoring, and reporting mechanisms, financial institutions and regulatory bodies work together to safeguard the integrity of the financial ecosystem and combat the ever-evolving threats posed by money laundering activities.
The Objectives of AML
The primary objectives of Anti Money Laundering (AML) encompass several key aspects:
- Detection and Prevention: AML endeavours to actively detect and prevent the circulation of illicit funds within financial institutions and other regulated entities. By implementing robust monitoring systems and conducting thorough due diligence, organisations aim to identify and thwart suspicious activities associated with money laundering.
- Reporting Suspicious Transactions: A crucial objective of AML is to establish effective mechanisms for reporting suspicious transactions to the appropriate authorities. Timely and accurate reporting enables regulatory bodies to investigate potential instances of money laundering, ensuring that illicit activities are promptly addressed.
- Compliance and Enforcement: AML strongly emphasises compliance with regulatory frameworks. Financial institutions and other entities are expected to adhere to AML regulations and guidelines to maintain the financial system's integrity. Non-compliance may result in penalties and enforcement actions, underscoring the importance of robust compliance measures.
By diligently pursuing these objectives, AML aims to create a robust and resilient financial environment that is fortified against the risks posed by money laundering. The proactive detection and prevention of illicit financial activities, coupled with rigorous reporting and compliance measures, contribute to the overarching goal of safeguarding the integrity of the global financial system.
AML and KYC Regulations
The Interplay Between AML and KYC
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) are intrinsically linked in their goals and implementation. While KYC centres on customer identification and risk assessment, AML regulations establish a comprehensive framework to combat money laundering and various financial crimes. KYC plays a vital role in AML compliance by enabling the meticulous collection of precise customer information and assisting in the identification of potentially suspicious activities. By integrating KYC practices within AML frameworks, financial institutions and businesses can enhance their ability to identify and mitigate the risks associated with illicit financial transactions, thus bolstering the integrity of the global financial system.
Regulatory Frameworks
AML and KYC compliance is subject to the oversight of numerous international, regional, and national regulatory frameworks, which encompass the following:
- Financial Action Task Force (FATF) Recommendations: The FATF, a prominent global organisation, has established comprehensive standards and recommendations that guide AML and KYC practices worldwide. These recommendations are continuously updated to address evolving risks and challenges in the financial sector.
- The USA PATRIOT Act: Enacted in the United States, the USA PATRIOT Act introduced robust measures and stringent AML and KYC requirements for financial institutions operating within the country. This legislation aims to combat money laundering, terrorist financing, and other illicit activities, thereby safeguarding the integrity of the U.S. financial system.
- European Union Directives: The European Union has implemented several directives, including the Fourth and Fifth Money Laundering Directives, to enhance AML and KYC practices across EU member states. These directives outline specific obligations and measures that financial institutions must adhere to in order to mitigate the risks associated with money laundering and terrorist financing within the European Union.
Financial institutions and businesses can ensure robust AML and KYC compliance, promote transparency, and contribute to global efforts to combat financial crimes by adhering to these internationally recognised frameworks and national legislations. The collaboration between regulatory authorities and the implementation of comprehensive regulations are crucial in establishing a resilient and secure financial environment on a global scale.
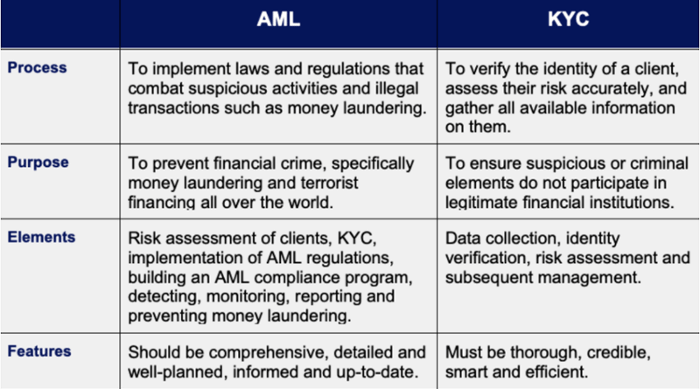
Differences between AML and KYC
Focus and Scope
The primary objective of Anti Money Laundering (AML) is to address the detection and prevention of money laundering activities comprehensively. AML encompasses a broad spectrum of measures aimed at combating various financial crimes, including but not limited to terrorist financing and fraudulent activities. On the other hand, Know Your Customer (KYC) primarily emphasises customer identification and risk assessment. KYC serves as a crucial component of AML by enabling thorough customer due diligence processes. By adopting robust KYC practices, financial institutions and businesses can effectively evaluate the risks associated with their customers, thereby enhancing their ability to detect and prevent potential illicit activities. The integration of AML and KYC frameworks establishes a strong defence against financial crimes, promoting transparency and safeguarding the integrity of the global financial system.
Implementation
Anti Money Laundering (AML) regulations are rigorously enforced by regulatory bodies to ensure the integrity of the financial system. These regulations necessitate that financial institutions and other entities establish comprehensive AML programs to combat the risks associated with money laundering and other illicit activities. In parallel, Know Your Customer (KYC) is an essential process that these institutions implement as a vital component of their AML compliance measures. By incorporating robust KYC practices into their AML frameworks, financial institutions can effectively identify and verify the identities of their customers, assess their risk profiles, and proactively mitigate the potential threats posed by money laundering. The integration of AML regulations and KYC processes reinforces the overall resilience of the financial ecosystem, upholding transparency and safeguarding against illicit financial activities.
Obligations and Requirements
Anti Money Laundering (AML) regulations encompass a range of legal obligations that financial institutions must adhere to. These regulations necessitate reporting suspicious transactions, ongoing monitoring of customer activities, and establishing robust record-keeping practices. In parallel, Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements are critical to AML compliance. KYC entails a series of procedures, including customer identification, verification, and risk assessment. By implementing comprehensive KYC processes, financial institutions gather essential information and conduct thorough due diligence to effectively identify and mitigate risks associated with money laundering and other financial crimes. The integration of KYC within AML frameworks empowers institutions to enhance their ability to detect, prevent, and combat illicit activities, safeguarding the integrity of the financial system. Through stringent AML regulations and robust KYC practices, financial institutions contribute to the collective efforts aimed at maintaining transparency, integrity, and security in the global financial landscape.
Where and When KYC and AML are Required?
Financial Institutions
Banks, credit unions, insurance companies, brokerage firms, and various other financial institutions fall under Anti Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations. These regulations mandate the implementation of robust AML programs and the execution of KYC procedures by these institutions. AML programs are designed to combat money laundering, terrorist financing, and other illicit activities, ensuring the financial system's integrity. Simultaneously, KYC procedures are employed by financial institutions to gather vital customer information, verify identities, assess risks, and establish trustworthiness. Financial institutions are obliged to adhere to these regulations when establishing new customer relationships, conducting high-value transactions, and identifying suspicious activities. By incorporating comprehensive AML programs and rigorous KYC procedures, financial institutions contribute to the collective efforts of combating financial crimes and safeguarding the integrity of the global financial landscape.
Non-Financial Businesses and Professions
In addition to financial institutions, specific non-financial businesses and professions have a pivotal role in upholding Anti Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements. This regulatory framework extends its reach to entities such as real estate agents, lawyers, accountants, and high-value goods dealers. These non-financial entities bear the responsibility of implementing AML and KYC measures to counter money laundering activities effectively.
By conducting thorough customer due diligence procedures, verifying identities, and assessing the legitimacy of transactions, these entities contribute to preventing and detecting illicit financial activities. Moreover, they are an essential link in the information-sharing network, promptly reporting suspicious transactions to the relevant authorities. By aligning themselves with AML and KYC requirements, these non-financial businesses and professions fortify the collective efforts of combating money laundering and maintaining the financial system's integrity.

Cross-Border Transactions
AML and KYC measures become particularly important in cross-border transactions. Financial institutions must exercise heightened due diligence when dealing with foreign customers, correspondent banking relationships, and transactions involving high-risk jurisdictions.
Emerging Technologies and KYC/AML Compliance
Rapid technological advancements have ushered in a new era of AML and KYC compliance, revolutionizing the way financial institutions approach regulatory requirements. These institutions are embracing cutting-edge technologies to propel their compliance processes to unprecedented heights. Let's delve into some of the remarkable technological innovations that are reshaping the AML and KYC landscape:
- Harnessing the Power of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: AI-driven systems are at the forefront of transforming compliance practices. By analyzing vast volumes of customer data, these intelligent systems can identify complex patterns, detect potential risks, and swiftly recognize suspicious activities that might otherwise go unnoticed. The integration of AI and machine learning algorithms equips financial institutions with powerful tools to combat money laundering and maintain regulatory compliance.
- Embracing Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Robotic Process Automation is automating KYC processes, offering a multitude of benefits to financial institutions. By deploying intelligent software robots, institutions can streamline and expedite KYC procedures, significantly reducing the time and effort required for manual tasks. RPA ensures enhanced accuracy, mitigates the risk of human errors, and frees up valuable resources that can be redirected to more critical compliance tasks.
- Exploring the Potential of Blockchain Technology: Blockchain, the transformative technology underlying cryptocurrencies, holds immense promise in the realm of AML and KYC compliance. Its decentralized and tamper-proof nature provides a secure and immutable record of transactions. By leveraging blockchain, financial institutions can establish a transparent and auditable ledger, ensuring enhanced traceability of funds and bolstering the fight against illicit activities. The integration of smart contracts on the blockchain further automates compliance processes, ensuring adherence to predefined rules and enhancing efficiency.
- Biometric Authentication and Identification: Biometric technologies such as fingerprint scanning, facial recognition, and voice authentication are gaining traction in the AML and KYC landscape. These advanced methods provide robust customer identification and verification capabilities, adding an extra layer of security and accuracy to the compliance process. Biometric authentication enhances the reliability of customer data, reduces the risk of identity theft, and enables seamless and convenient onboarding experiences for customers.
As technology continues to advance, financial institutions are embracing these innovative solutions to strengthen their AML and KYC compliance efforts. By harnessing the power of AI, RPA, blockchain, and biometrics, they are equipping themselves with the tools needed to stay ahead of emerging threats, ensure regulatory compliance, and safeguard the financial system's integrity. The symbiotic relationship between technology and compliance is shaping a new era of efficiency, accuracy, and effectiveness in the fight against financial crimes.
Final Thoughts
AML and KYC compliance are indispensable in today's financial landscape, serving as crucial tools in combating money laundering, terrorist financing, and other financial crimes. While AML focuses on preventing illicit activities, KYC forms the foundation of due diligence by accurately identifying customers and assessing risks. Financial institutions and businesses must adhere to regulatory frameworks, implement comprehensive AML programs, and conduct KYC procedures to maintain the financial system's integrity. Leveraging technological advancements further enhances compliance efforts and strengthens the fight against financial crimes. By effectively implementing AML and KYC measures, we can create safer and more transparent financial systems.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the consequences of non-compliance with AML and KYC regulations?
Non-compliance with AML and KYC regulations can result in severe penalties, including hefty fines, reputational damage, loss of license, and criminal charges for individuals involved in illicit activities.
2. How often should KYC be updated?
KYC information should be regularly updated based on risk assessment. High-risk customers may require more frequent updates, while low-risk customers can be reviewed less frequently.
3. Are there global standards for AML and KYC compliance?
Yes, the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) sets global standards and provides AML and KYC compliance recommendations. Many countries align their regulations with FATF standards.
4. How can technology assist in AML and KYC compliance?
Technology can automate processes, analyze data, and identify suspicious patterns more efficiently. It enables financial institutions to streamline compliance efforts and detect potential risks more effectively.
5. Who is responsible for AML and KYC compliance?
Financial institutions and businesses subject to AML and KYC regulations bear the responsibility for ensuring compliance. This includes implementing robust AML programs, conducting KYC procedures, and training employees on compliance obligations.
Anti-Financial Crime Compliance with Tookitaki?



