Bank Secrecy Act or BSA: The cornerstone of AML regulation in the US
Introduction to the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA)
The Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) is a crucial piece of legislation in the United States designed to combat money laundering, terrorist financing, and other financial crimes. Enforced by the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), the BSA imposes certain requirements on financial institutions to promote transparency and maintain the integrity of the financial system.
In this article, we will delve into the Bank Secrecy Act, its requirements, its role in anti-money laundering (AML) efforts, and the significance of compliance for financial institutions. Join us as we explore the world of the Bank Secrecy Act and its impact on the banking industry.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the Bank Secrecy Act and its requirements can be challenging. Simplifying the complex regulations is essential to ensure effective compliance and mitigate potential risks.
- The Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) is a U.S. federal law aimed at preventing money laundering, terrorist financing, and other financial crimes.
- BSA requirements include establishing a Customer Identification Program (CIP), filing Currency Transaction Reports (CTRs), and submitting Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs).
- Compliance with the Bank Secrecy Act is crucial for financial institutions to promote financial transparency and protect the integrity of the financial system.
- Non-compliance with BSA requirements can result in severe penalties and reputational damage for financial institutions.
Purpose and Objectives of the Bank Secrecy Act
The Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) serves as a crucial safeguard against money laundering, terrorist financing, and other financial crimes in the United States. By enforcing requirements such as the Customer Identification Program (CIP), Currency Transaction Reports (CTRs), and Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs), financial institutions play a vital role in promoting transparency and maintaining the integrity of the financial system. Compliance with the BSA is not only essential for mitigating risks and protecting reputations but also for upholding the responsibilities of financial institutions in contributing to a secure and transparent financial ecosystem.
BSA Requirements for Financial Institutions
Banks and other financial institutions in the US are mandated to fulfil certain obligations under the BSA. They include implementing a risk-based AML program with effective customer due diligence (CDD) and screening procedures. The institutions are also required to do a range of reporting and record-keeping when they deal with suspicious transactions and customers involved in potential money laundering and other crimes. Those who fail to comply with the BSA AML regulations are sanctioned. The major provisions of the BSA are the following:
- Recordkeeping and reporting requirements by private individuals, banks and other financial institutions
- Measures to identify the source, volume, and movement of currency and other monetary instruments transported or transmitted into or out of the US or deposited in financial institutions
- Requirements for banks to:
- (1) report cash transactions over $10,000 using the Currency Transaction Report (CTR)
- (2) properly identify persons conducting transactions
- (3) maintain a paper trail by keeping appropriate records of financial transactions
Financial institutions, including banks, credit unions, and other entities, are subject to various BSA requirements to ensure compliance and prevent illicit activities. Key requirements include:
- Customer Identification Program (CIP): Financial institutions must establish a CIP to verify the identity of customers opening accounts.
- Currency Transaction Reports (CTRs): Financial institutions are required to file CTRs for transactions involving more than a specified amount of currency, helping detect and track potential money laundering activities.
- Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs): Financial institutions must file SARs for suspicious transactions that may indicate money laundering, terrorist financing, or other illegal activities.
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Programs: Financial institutions must develop and implement AML programs, including internal controls, risk assessments, and ongoing monitoring to detect and prevent money laundering.
Bank Secrecy Act Reporting Requirements
- Currency Transaction Reports (CTRs): Financial institutions must file CTRs with FinCEN for cash transactions exceeding a specified threshold, providing valuable information for law enforcement and regulatory agencies.
- Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs): Financial institutions must file SARs to report any suspicious activity that may indicate potential money laundering, terrorist financing, or other illicit activities.
Significance of Compliance with the Bank Secrecy Act
BSA compliance or BSA AML compliance refers to financial institutions’ adherence to the provisions and requirements of the BSA so that the US financial system is not abused for criminal activities. As the designated administrator of the BSA, the FinCEN states its mission is to “safeguard the financial system from the abuses of financial crime, including terrorist financing, money laundering and other illicit activity.”
FinCEN ensures that financial institutions are adhering to BSA/AML Compliance norms and makes regular checks if they fulfil the three main AML requirements of the BSA.
The three main AML requirements of the BSA are:
- Reporting cash transactions over a set threshold using the Currency Transaction Report (CTR)
- Proper identification of those conducting transactions
- Keeping appropriate and necessary records of financial transactions to maintain an accurate paper trail
Bank Secrecy Act and Anti-Money Laundering (AML)
- Combating Money Laundering: The Bank Secrecy Act plays a vital role in the fight against money laundering by requiring financial institutions to implement robust AML programs, conduct due diligence, and report suspicious activities.
- Identifying and Reporting Suspicious Activities: Financial institutions must diligently monitor customer transactions and promptly report any suspicious activities through SAR filings, contributing to the early detection and prevention of financial crimes.
BSA AML Compliance Programme
In order to build an effective BSA AML Compliance Program, financial institutions need to ensure that they follow the BSA/AML pillars. The following are the five pillars of BSA AML Compliance.
1. Internal controls
It involves examining factors like geographic location, types of services offered, and customers served to mitigate the risk of money laundering. Internal controls vary based on the type of financial institution. A small credit union in the US will have entirely different internal controls compared to a nation-wide banking chain.
2. Designation of a BSA AML officer
Every financial institution should have a designated BSA/AML compliance officer who has ample experience in BSA AML compliance. The officer should be able to identify weak areas in the institution’s business plan and operations.
3. Establishment of BSA AML training programme
The compliance officer should also establish a BSA AML training program and to train all institutional staff.
4. Independent testing of compliance programme
Every financial institution should test their BSA/AML compliance program on an annual basis by involving a third party. This will help spot gaps in the compliance policy and direct institutions to take remedies if needed.
5. Customer due diligence (CDD)
CDD requires financial institutions to verify a customer’s identity, assess their AML/CFT risk, comprehend their financial habits, and ensure procedures to catch abnormalities.
All these five pillars together form the core of a successful BSA AML compliance programme.
Record keeping & reporting requirements under BSA
In order to ensure robust BSA AML compliance, financial institutions are required to keep detailed records of suspicious activities. They must maintain a log of purchases of monetary instruments including travellers’ checks and cashiers’ checks of between US$3,000 –10,000. The log should have verified the identities of purchasers with the aggregated value of their transactions.
The BSA also mandates financial institutions to do a number of reporting and filings with FinCEN when they encounter potential AML activities. These obligations are detailed in the following table.
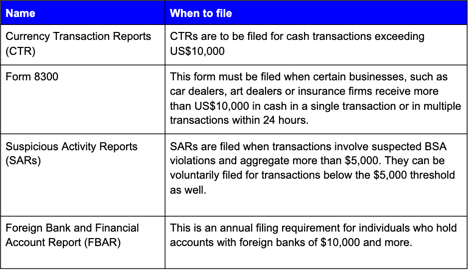
Most of these reports can be filed electronically, using FinCEN’s BSA e-Filing system. Organisations are required to submit a formal application to FinCEN to obtain access to the e-Filing system.
How Can Tookitaki Help With Compliance Regulations?
Non-compliance with compliance regulations such as the BSA could be detrimental to financial institutions' business in a number of ways. Failing to properly file CTRs and SARs, would lead to heavy fines and regulatory restrictions, including charter revocation, and even prison sentences for staff responsible. In 2018, U.S. Bancorp was fined $613 million for willful violations of the Bank Secrecy Act. Apart from the financial losses, non-compliance can tarnish an institution’s reputation in front of customers, investors and employees. Often, it takes many years to rebuild the damage caused to the reputation.
In order to comply with regulations, financial institutions resort to many software solutions that analyse transactions based on specified rules and come up with SAR filing suggestions. Today, modern technologies like AI and machine learning are being used in regulatory compliance. Compared to legacy solutions, AI-based solutions can significantly improve both process efficiency and compliance effectiveness.
Tookitaki has developed an end-to-end AML compliance platform called FinCense. It offers multiple solutions catering to the core AML activities such as transaction monitoring, name screening, transaction screening and customer risk scoring. Powered by advanced machine learning, FinCense addresses market needs and provides an effective and scalable BSA AML compliance solution. For a free demo of Tookitaki's FinCense, book a meeting with our experts by clicking below.
Anti-Financial Crime Compliance with Tookitaki?





